ديموغرافية الهند
بعد الصين، تحتل الهند المرتبة الثانية في العالم من حيث تعداد السكان. تمثل اللغة، الدين، والطبقات عوامل فاصلة في التنظيم الاجتماعي والسياسي للشعب الهندي. مدينة مومباي (بومباي سابقا) هي أهم تجمع حضري، بالإضافة إلى دلهي، كلكتا، وچـِنـّاي (مدراس سابقا).
| ديموغرافيا {{{place}}} | |
|---|---|
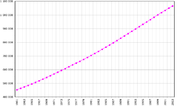 عدد سكان الهند, 1961-2003 | |
| السكان | 1,129,866,154 (2007 est) |
| معدل النمو | 1.38% (2007 est) |
| معدل المواليد | 22.69 births/1,000 population (2007 est) |
| معدل الوفيات | 6.58 deaths/1,000 population (2007 est) |
| العمر المتوقع | 68.59 years (2007 est) |
| • الذكور | 66.28 years (2007 est) |
| • الإناث | 71.17 years (2007 est) |
| معدل الخصوبة | 2.7 children born/woman (NFHS-3, 2007) |
| التركيبة العمرية | |
| 0–14 سنة | 31.5% (male 189,238,487/female 172,168,306)(2008 est) |
| 15–64 سنة | 63.3% (male 374,157,581/female 352,868,003) (2008 est) |
| 65 وأكثر | 5.2% (male 28,285,796/female 31,277,725) (2008 est) |
| النسبة بين الجنسين | |
| عند الميلاد | 1.12 male(s)/female (2008) |
| تحت 15 | 1.10 male(s)/female (2008) |
| 15–64 سنة | 1.06 male(s)/female (2008) |
| الجنسية | |
| الجنسية | noun: Indian adjective: Indic |
| الأغلبية العرقية | انظر Ethnic Groups of India |
| اللغة | |
| الرسمية | انظر اللغات الرسمية في الهند |
| المنطوقة | انظر قائمة لغات الهند حسب المتحدثين الأصليين بها |
نسبة التعليم في الهند تقارب 64.8%، 53.7% من النساء و75.3% من الرجال. نسبة الذكور إلى الإناث هي 1000 إلى 933. نسبة العاملين إلى إجمالي السكان 39.1%، أما حسب الجنس فتتوزع النسب كالآتي: الرجال 51.7%، والنساء 25.6%. متوسط الحياة 22.66 سنة، فيما بلغت نسبة المواليد 2.23%.
بالإضافة إلى الهندو والذين يشكلون حوالي 80% من التركيبة العرقية للشعب الهندي، تعتبر البلاد ثاني أكبر دولة إسلامية بعد أندوسيا، وتبلغ نسبة المسلمين فيها 13.4% (أو أكثر حسب بعض المصادر الأخرى). تتواجد أقليات دينية أخرى على غرار، المسيحيين (2.33%)، السيخ (1.84%)، البوذيين (0.76%) وغيرهم.
الهند موطن اثنين من العائلات اللغوية الرئيسية، الهندو-آرية والدرافيدية. يعترف الدستور الهندي باثنين وثلاثين لغة -اللغات الرسمية-. تستعمل الحكومة المركزية اللغتين الهندية والإنكليزية في المراسيم والمناسبات الرسمية. تاريخيا تعتبر اللغتين السنسكريتية والتاميلية لغات أصيلتان، لأنهما ظهرتا على الأرض الهندية. يبلغ عدد اللهجات المحلية في الهند 1652 لهجة.
| الترتيب | مدينة أساسية | الولاية | التعداد | الترتيب | مدينة أساسية | الولاية | التعداد | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ممباي | مهارشترا | 13,662,885 | 11 | جايپور | راجاستان | 2,997,114 | |
| 2 | دلهي | دلهي | 11,954,217 | 12 | لكنو | اوتار پرادش | 2,621,063 | |
| 3 | بنگالورو | كرناتكا | 5,180,533 | 13 | دانباد | جهارخند | 2,394,434 | |
| 4 | كلكتا | البنغال الغربية | 5,021,458 | 14 | ناگپور | مهارشترا | 2,359,331 | |
| 5 | چـِنـّاي | تاميل نادو | 4,562,843 | 15 | إندوره | ماديا پرادش | 1,768,303 | |
| 6 | حيدر أباد | أندرا پرادش | 3,980,938 | 16 | پاتنا | بيهار | 1,753,543 | |
| 7 | أحمد أباد | گجرات | 3,867,336 | 17 | بهوبال | ماديا پرادش | 1,742,375 | |
| 8 | پونه | مهارشترا | 3,230,322 | 18 | ثانه | مهارشترا | 1,673,465 | |
| 9 | سورات | گجرات | 3,124,249 | 19 | لوديانا | پنجاب | 1,662,325 | |
| 10 | كانپور | اوتار پرادش | 3,067,663 | 20 | أگرا | اوتار پرادش | 1,686,975 | |
| ملاحظة:هذه هي قائمة تعدادات مدن ولا تعطي تعداد التجمعات الحضرية | ||||||||
| الترتيب هو حسب التعداد (حساب 2010)[1] | ||||||||
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
تعداد السكان
ديموغرافيا دينية
80.5% من الهنود هندوس ونسبة 13.4% مسلمون وتعتبر الهند ثالث أكبر دولة من حيث عدد المسلمين في العالم بعد اندونيسيا و باكستان. ويوجد في الهند أيضا العديد من الديانات الأخرى. وبها نسبة 2.3% من المسيحيين, 0.8% بوذيين, و0.4% يهود.
| Composition | Hindus[2] | Muslims[3] | Christians[4] | Sikhs[5] | Buddhist[6] | Jains[7] | Others[8] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % total of population 2005 | 80.4% | 13.4% | 2.3% | 1.9% | 1.1% | 0.4% | 0.5% |
| 10-Yr Growth % (est '91–'01)[9][β] | 20.3% | 29.5% | 22.6% | 18.2% | 24.5% | 26.0% | 103.1% |
| Sex ratio* (avg. 944) | 935 | 940 | 1009 | 895 | 955 | 940 | 100 |
| Literacy rate (avg. 79.9) | 75.5 | 60.0 | 90.3 | 70.4 | 73.0 | 95.0 | 50.0 |
| Work Participation Rate | 40.4 | 31.3 | 39.7 | 37.7 | 40.6 | 32.9 | 48.4 |
| Rural sex ratio[9] | 944 | 953 | 1001 | 895 | 958 | 937 | 995 |
| Urban sex ratio[9] | 922 | 907 | 1026 | 886 | 944 | 941 | 966 |
| Child sex ratio (0–6 yrs) | 925 | 950 | 964 | 786 | 942 | 870 | 976 |
α. ^ The data excludes Mao-Maram, Paomata and Purul subdivisions of Senapati District of Manipur
β. ^ The data is "unadjusted" (without excluding Assam and Jammu and Kashmir); 1981 census was not conducted in Assam and 1991 census was not conducted in Jammu and Kashmir
ديموغرافية لغوية
| Rank | Language | 2001 census[1] (total population 1,004.59 million) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| المتحدثين | النسبة | ||
| 1 | Hindi dialects[10] | 422,048,642 | 41.03% |
| 2 | Bengali | 83,369,769 | 8.11% |
| 3 | Telugu | 74,002,856 | 7.37% |
| 4 | Marathi | 71,936,894 | 6.99% |
| 5 | Tamil | 60,793,814 | 5.91% |
| 6 | Urdu | 51,536,111 | 5.01% |
| 7 | Gujarati | 46,091,617 | 4.48% |
| 8 | Kannada | 37,924,011 | 3.69% |
| 9 | Malayalam | 33,066,392 | 3.21% |
| 10 | Oriya | 33,017,446 | 3.21% |
| 11 | Punjabi | 29,102,477 | 2.83% |
| 12 | Assamese | 13,168,484 | 1.28% |
| 13 | Maithili | 12,179,122 | 1.18% |
| 14 | Santali | 6,469,600 | 0.63% |
| 15 | Kashmiri | 5,527,698 | 0.54% |
| 16 | Nepali | 2,871,749 | 0.28% |
| 17 | Sindhi | 2,535,485 | 0.25% |
| 18 | Konkani | 2,489,015 | 0.24% |
| 19 | Dongri | 2,282,589 | 0.22% |
| 20 | Meitei (Manipuri) | 1,466,705* | 0.14% |
| 21 | Bodo | 1,350,478 | 0.13% |
| 22 | Sanskrit | 14,135 | N |
احصائيات ديموغرافية
Total Population: 1,147.996 million (July 2008 est. CIA)[12] 1,028.7 million (2001 Census final figures, March 1 enumeration and estimated 124,000 in areas of Manipur that could not be covered in the enumeration)
Rural Population: 72.2%, male: 381,668,992, female: 360,948,755 (2001 Census)
Urban Population:
Age structure:
0–14 years: 30.8%, male: 188,208,196, female: 171,356,024
15–64 years: 64.3%, male: 386,432,921, female: 364,215,759
65+ years: 4.9%, male: 27,258,259, female: 30,031,289 (2007 est.)
The median age of Indians is 25.1 years.
Population growth rate: 1.38% (2007 est.)
Birth rate: 22.69 births/1,000 population (2007 est.)
Death rate: 6.58 deaths/1,000 population (2006 est.)
Literacy rate: 79.9%
Percent of the population under the poverty line: 22% (2006 est.)
Unemployment Rate: 7.8%
Net migration rate: − -0.05 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2007 est.)
Sex ratio:
at birth:
1.12 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.098 male(s)/female
15–64 years:
1.061 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.908 male(s)/female
total population:
1.064 male(s)/female (2006 est.)
Infant mortality rate: total: 34.61 deaths/1,000 live births (2007 est.) female: 29.23 deaths/1,000 live births male: 39.42 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth:
total population:
68.59 years
male:
66.28 years
female:
71.17 years (2007 est.)
Total fertility rate: 2.81 children born/woman (2007 est.) The TFR (Total number of children born per women ) according to Religion in 2001 was :
Hindus - 2.0, Muslims - 2.4, Sikhs - 1.6, Christians - 2.1, Buddhists - 2.1, Jains - 1.4 , Animists and Others - 2.99, Tribals - 3.16, Scheduled Castes - 2.89.[بحاجة لمصدر]
Nationality:
noun:
Indian(s)
adjective:
Indian
Religions: Hindu 80.5%, Muslim 13.4%, Christian 2.3%, Sikh 1.8%, Buddhists 0.8%, Jains 0.4%, others 0.7%, unspecified 0.1% (2001 Census) [13][14] [15][16].
Scheduled Castes and Tribes: Scheduled Castes: 16.2% (2001 Census) Scheduled Tribes: 8.2% (2001 Census)
Languages: See Languages of India and List of Indian languages by total speakers. There are 216 languages with more than 10,000 native speakers in India. The largest of these is Hindi with some 337 million (the second largest being Bengali with some 207 million). 22 languages are recognized as official languages. In India, there are 1,652 languages and dialects in total.[17][18]
2025 Estimate
Table 2: Population Projections (in millions)
| Year | Under 15 | 15-64 | 65+ | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 361 | 604 | 45 | 1010 |
| 2005 | 368 | 673 | 51 | 1093 |
| 2010 | 370 | 747 | 58 | 1175 |
| 2015 | 372 | 819 | 65 | 1256 |
| 2020 | 373 | 882 | 76 | 1331 |
Source: Based on P.N. Mari Bhat, "Indian Demographic Scenario 2025", Institute of Economic Growth, New Delhi, Discussion Paper No. 27/2001.
المجموعات العرقية
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
قراءات إضافية
- International Institute for Population Sciences and Macro International (2007-09-09). "Summary of Findings" (PDF). Third National Family Health Survey. International Institute for Population Sciences.
انظر أيضا
وصلات خارجية
- Census of India; Govt. site with detailed data from 2001 census
- Census of India map generator; generates maps based on 2001 census figures
- Census-2001 Religion wise data
- Demographic data for India; provides sources of demographic data for India
- Peopling of India
- Kokrajhar District Information Gateway - Census 2001
- Population Explosion in West Bengal: A Survey A Study by South Asia Research Society, Calcutta
- indianchild.com - Population of India
- District Level Estimates of Fertility from India’s 2001 Census
المصادر
- ^ Largest cities and towns and statistics of their population World gazetteer
- ^ "Tables: Profiles by main religions: Hindus". Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 2008-11-26.
- ^ "Tables: Profiles by main religions: Muslims". Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 2008-11-26.
- ^ "Tables: Profiles by main religions: Christians". Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 2008-11-26.
- ^ "Tables: Profiles by main religions: Sikhs". Census of India 2001: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 2008-11-26.
- ^ "Tables: Profiles by main religions: Buddhists". Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 2008-11-26.
- ^ "Tables: Profiles by main religions: Jains". Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 2008-11-26.
- ^ "Tables: Profiles by main religions: Other religions". Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 2008-11-26.
- ^ أ ب ت "Census of India". Census of India. Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 2008-11-26.
- ^ includes Western Hindi, Eastern Hindi, Bihari languages, Rajasthani languages and Pahari languages.
- ^ National Population Policy of India
- ^ CIA World Factbook - India
- ^ Religious Composition Census of India: Census Data 2001: India at a glance >> Religious Composition. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved on 2008-11-26.
- ^ International Religious Freedom Report 2007-India International Religious Freedom Report 2007. U.S. Department of State.
- ^ CIA's The World Factbook - India
- ^ Bureau of South and Central Asian Affairs - Background Note: India
- ^ Mother Tongues of India According to the 1961 Census
- ^ Rupert Goodwins. Smashing India's language barriers. ZDNet UK.

