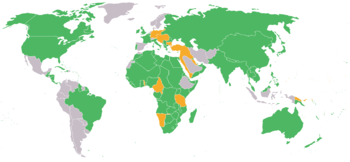
حلفاء الحرب العالمية الأولى
حلفاء الحرب العالمية الأولى Allies of World War I، ويُعرفوا أيضاً بإسم قوى الوفاق، كانوا البلدان التي عارضت القوى المركزية أثناء الحرب العالمية الأولى.
حلفاء الحرب العالمية الأولى قوى الوفاق | |
|---|---|
| 1914–1918 | |
| |
| المكانة | تحالف عسكري |
| الحقبة التاريخية | الحرب العالمية الأولى |
• تأسست | 1914 |
• انحل | 1918 |
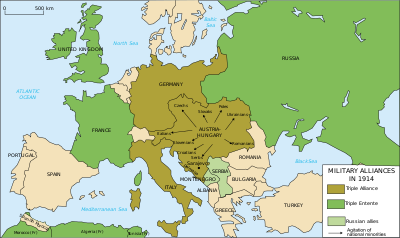
أعضاء تحالف الوفاق الأصلي المبرم في 1907 كانوا الجمهورية الفرنسية، والامبراطورية البريطانية والامبراطورية الروسية. إيطاليا أنهت تحالفها مع القوى المركزية، متعللة بأن ألمانيا والنمسا-المجر بدآ الحرب وأن التحالف كان بطبيعته دفاعياً فقط؛ وبذلك فقد أنهت الحرب في جانب الوفاق في 1915. كما كانت اليابان عضواً هاماً. بلجيكا وصربيا واليونان والجبل الأسود ورومانيا[1] كن أعضاء ثانويين في الوفاق.[2]
معاهدة سيڤر في 1920 عرّفت القوى المتحالفة الرئيسية كالتالي: الامبراطورية البريطانية، والجمهورية الفرنسية وإيطاليا واليابان. القوى المتحالفة ضمت – مع القوى التحالفة الرئيسية – أرمينيا وبلجيكا واليونان والحجاز وپولندا والبرتغال ورومانيا والدولة الصربو-كروانية-سلوڤينية وتشيكوسلوڤاكيا.[3]
الولايات المتحدة أعلنت الحرب على ألمانيا في أبريل 1917 على أساس أن ألمانيا انتهكت حياد الولايات المتحدة بمهاجمة سفن الشحن العالمي وبسبب برقية زيمرمان المرسلة إلى المكسيك.[4] It declared war on Austria-Hungary in December 1917.[5][6] The U.S. entered the war as an "associated power", rather than as a formal ally of France and the United Kingdom, in order to avoid "foreign entanglements".[7] Although the Ottoman Empire and Bulgaria severed relations with the United States, neither declared war on her.[8]
بالرغم من أن الدومنيونات ومستعمرات التاج في الامبراطورية البريطانية قاموا مساهمات بارزة في المجهود الحربي للحلفاء، إلا أنه لم يكن لديهم independent foreign policies during World War I. The five-member British War Cabinet (BWC) exercised operational control of British Empire forces. However, the Dominion governments controlled recruiting, and did remove personnel from front-line duties as they saw fit.
ومنذ مطلع 1917 the BWC was superseded by the مجلس وزراء الحرب الامبراطوري, which had Dominion representation. الفيلق الأسترالي والفيلق الكندي were placed for the first time under the command of Australian and Canadian Lieutenant Generals John Monash and Arthur Currie,[9] respectively, who reported in turn to British generals.[بحاجة لمصدر] In April 1918 operational control of all Entente forces on the الجبهة الغربية passed to the new supreme commander, فردينان فوش من فرنسا.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
التاريخ
The original alliance opposed to the Central Powers was the الوفاق الثلاثي, which was formed by three Great European Powers:
The war began with the Austrian attack invasion of Serbia on 28 July 1914, in response to the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The Austrian Empire followed with an attack on the Serbian ally Montenegro on 8 August.[بحاجة لمصدر] On the Western Front, the two neutral States of Belgium and Luxembourg were immediately occupied by German troops as part of the German Schlieffen Plan.
Of the two Low Countries involved in the war, Luxembourg chose to capitulate, and was viewed as a collaborationist state by the Entente powers: Luxembourg never became part of the Allies, and only narrowly avoided Belgium's efforts of annexation, at the conclusion of hostilities in 1919. On 23 August Japan joined the Entente, which then counted seven members.[بحاجة لمصدر]. The entrance of the British Empire brought Nepal into the war.
On 6 April 1917, the United States entered the war. Liberia, Siam and Greece also became allies. After the October Revolution, Russia left the alliance and ended formal involvement in the war, by the signing of the treaty of Brest Litovsk in November effectively creating a separate peace with the Central Powers. This was followed by Romanian cessation of hostilities, however the Balkan State declared war on Central Powers again on 10 November 1918. The Russian withdrawal allowed for the final structure of the alliance, which was based on five Great Powers:
Following the Versailles conference, Britain, France, Italy and Japan became the permanent members of the League of Nations council. The United States, meant to be the fifth permanent member, left because the US Senate voted on 19 March 1920 against the ratification of the Treaty of Versailles, thus preventing American participation in the League.
| التعداد (بالملايين) |
الأرض (مليون كم²) |
GDP (بليون $) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| الموجة الأولى: 1914 | ||||||
| روسيا | الامبراطورية الروسية (بما فيها پولندا) | 173.2 | 21.7 | 257.7 | ||
| Finland | 3.2 | 0.4 | 6.6 | |||
| الاجمالي | 176.4 | 22.1 | 264.3 | |||
| الجمهورية الفرنسية الثالثة | فرنسا | 39.8 | 0.5 | 138.7 | ||
| المستعمرات الفرنسية | 48.3 | 10.7 | 31.5 | |||
| الاجمالي | 88.1 | 11.2 | 170.2 | |||
| الامبراطوية البريطانية | المملكة المتحدة | 46.0 | 0.3 | 226.4 | ||
| المستعمرات البريطانية | 380.2 | 13.5 | 257 | |||
| British Dominions | 19.9 | 19.5 | 77.8 | |||
| Total | 446.1 | 33.3 | 561.2 | |||
| Empire of Japan | Japan | 55.1 | 0.4 | 76.5 | ||
| Japanese colonies[11] | 19.1 | 0.3 | 16.3 | |||
| Total | 74.2 | 0.7 | 92.8 | |||
| Yugoslav states[12] | 7.0 | 0.2 | 7.2 | |||
| الموجة الثانية (1915–16) | ||||||
| Kingdom of Italy | Italy | 35.6 | 0.3 | 91.3 | ||
| Italian colonies | 2.0 | 2.0 | 1.3 | |||
| Total | 37.6 | 2.3 | 92.6 | |||
| Kingdom of Portugal | Portugal | 6.0 | 0.1 | 7.4 | ||
| Portuguese colonies | 8.7 | 2.4 | 5.2 | |||
| Total | 14.7 | 2.5 | 12.6 | |||
| Kingdom of Romania | 7.7 | 0.1 | 11.7 | |||
| الموجة الثالثة (1917–18) | ||||||
| الولايات المتحدة | United States | 96.5 | 7.8 | 511.6 | ||
| overseas dependencies[13] | 9.8 | 1.8 | 10.6 | |||
| Total | 106.3 | 9.6 | 522.2 | |||
| Central American states[14] | 9.0 | 0.6 | 10.6 | |||
| Brazil | 25.0 | 8.5 | 20.3 | |||
| Kingdom of Greece | 4.8 | 0.1 | 7.7 | |||
| Siam | 8.4 | 0.5 | 7.0 | |||
| Republic of China | 441.0 | 11.1 | 243.7 | |||
| Liberia | 1.5 | 0.1 | 0.9 | |||
| Population (millions) |
Territory (million km2) |
GDP ($ billion) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| November 1914 | |||||
| Allies, total | 793.3 | 76.5 | 1,096.5 | ||
| UK, France and Russia only | 259.0 | 22.6 | 622.6 | ||
| November 1916 | |||||
| Allies, total | 793.3 | 67.5 | 1,213.4 | ||
| UK, France and Russia only | 259.0 | 22.6 | 622.6 | ||
| November 1918 | |||||
| Allies, total | 1,271.7 | 80.8 | 1,760.5 | ||
| Percentage of world | 70% | 61% | 64% | ||
| UK, France and USA only | 182.0 | 8.7 | 876.6 | ||
| Percentage of world | 10% | 7% | 32% | ||
| Central Powers[16] | 156.1 | 6.0 | 383.9 | ||
| World, 1913 | 1,810.3 | 133.5 | 2,733.9 | ||
الدول الحلفاء المقاتلة الرئيسية
المملكة المتحدة
المسنعمرات والتوابع
في أوروپا
جبل طارق، Cyprus and Malta were British dependencies in Europe.
في أفريقيا
روسيا
فرنسا
اليابان
إيطاليا
الدول المؤازرة المقاتلة الأخرى
بلجيكا
Belgium had declared its neutrality when the war began, but Germany disregarded Belgium's neutrality and invaded the country in order to launch an offensive against the French capital of Paris. As a result, Belgium became a member of the Allies.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
البرازيل
Brazil entered the war in 1917 after the United States intervened on the basis of Germany's unrestricted submarine warfare sinking its merchant ships, which Brazil also cited as a reason to enter the war fighting against Germany and the Central Powers.
الجبل الأسود
Montenegro had very close cultural and political connections with Serbia and had cooperated with Serbia in the Balkan Wars of 1912–1913. Montenegro joined the war against Austria-Hungary.
نجد والأحساء
وافقت إمارة نجد والأحساء على دخول الحرب كحليف لبريطانيا في معاهدة دارين في 26 ديسمبر 1915.[17]
صربيا
Serbia was invaded by Austria-Hungary after Austria-Hungary placed a stringent ultimatum to the Serbian government demanding full compliance to an Austro-Hungarian investigation of complicity by the Serbian government in the assassination of Archduke Francis Ferdinand. Serbia agreed to most of Austria-Hungary's demands but because it did not fully comply, Austria-Hungary invaded.
الدول المؤازرة الرئيسية
الولايات المتحدة
Non-state combatants
Four non-state combatants, which voluntarily fought with the Allies and seceded from the constituent states of the Central Powers at the end of the war, were allowed to participate as winning nations to the peace treaties:
- Armenian irregulars and volunteers: seceded from Russia and fought against Ottoman Empire.
- Polish Legions
- Czechoslovak Legions: armed by France, Italy and Russia
- فلسطين: armed by Britain in Palestine
الزعماء
صربيا
- Peter I – King of Serbia
- Crown Prince Alexander – Regent, Commander-in-Chief
- Nikola Pašić – رئيس وزراء صربيا
- Field Marshal Radomir Putnik – Chief of the General Staff of the Serbian Army (1914–1915)
- General / Field Marshal Živojin Mišić – Deputy Chief of General Staff (1914), Commander of First Army (1914–1915; 1917), later Chief of General Staff (1918)
- General / Field Marshal Petar Bojović – Commander of First Army (1914), Deputy Chief of General Staff (1915–1916), Chief of General Staff (1916–1917) later Commander of First Army (1918)
- General / Field Marshal Stepa Stepanović – Commander of Second Army (1914–1918)
- General Pavle Jurišić Šturm – Commander of Third Army (1914–1916)
- Colonel Dušan Stefanović (sr) – Minister of War (1914)
- Colonel Radivoje Bojović – Minister of War (1914–1915)
- Colonel / General Božidar Terzić (sr) – Minister of War (1915–1918)
- General Mihailo Rašić (sr) – Minister of War (1918)
- Colonel / General Miloš Vasić (sr) – Commander of First Army (1916; 1917), Commander of Third Army (1916)
الجبل الأسود
- Nicholas I – King of Montenegro, Commander-in-Chief
- General Serdar Janko Vukotić – Prime Minister, Commander of 1st Montenegrin Army
- General Božidar Janković – Chief of the General Staff of the Montenegrin Army (1914–1915)
- Colonel Petar Pešić (sr) – Deputy Chief of the General Staff of the Montenegrin Army (1914–1915), later Chief of the General Staff of the Montenegrin Army (1915–1916)
- Crown Prince Danilo II Petrović-Njegoš – In the staff of the 1st Montenegrin Army
- Brigadier Krsto Popović – In the staff of the 1st Montenegrin Army, Aide-de-camp to Serdar Janko Vukotić
- General Anto Gvozdenović – King's Aide-de-camp
- General Mitar Martinović (sr) – Commander of several detachments in the Montenegrin army ( Drina and Herzegovina detachments together in 1914–1915, Kotor detachment in 1916 )
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
روسيا
- Nicholas II — Russian Emperor, King of Poland, and Grand Prince of Finland. (Until 15 March 1917)
- Grand Duke Nicholas Nikolaevich – Commander-in-chief (1 August 1914 – 5 September 1916) and viceroy in the Caucasus
- Ivan Goremykin – Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (1 August 1914 – 2 February 1916)
- Boris Stürmer – Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (2 February 1916 – 23 November 1916)
- Alexander Trepov – Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (23 November 1916 – 27 December 1916)
- Nikolai Golitsyn – Chairmen of Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire (27 December 1916 – 9 January 1917)
- General of the Cavalry Alexander Samsonov – Commander of the Russian Second Army for the invasion of East Prussia (1 August 1914 – 29 August 1914)
- General of the Cavalry Paul von Rennenkampf – Commander of the Russian First Army for the invasion of East Prussia (1 August 1914 – November 1914)
- General of the Artillery Nikolay Ivanov – Commander of the Russian army on the Southwestern Front, (1 August 1914 – March 1916) responsible for much of the action in Galicia
- General Adjutant Aleksei Brusilov – Commander of the South-West Front, then provisional Commander-in-Chief after the Tsar's abdication (February 1917 – August 1917)
- General of the Infantry Lavr Georgievich Kornilov – Commander of the South-West Front, then Commander-in-Chief (August 1917)
- General of the Infantry Aleksey Kuropatkin – Commander of the Northern Front (October 1915 – 1917)
- General of the Infantry Nikolai Yudenich – Commander of the Caucasus (January 1915 – May 1917)
- Admiral Andrei Eberhardt – Commander of Black Sea Fleet (1914–16)
- Admiral Alexander Kolchak – Commander of Black Sea Fleet (1916–17)
- Admiral Nikolai Essen – Commander of Baltic Fleet (1913 – May 1915)
بلجيكا
- Albert I of Belgium – King of the Belgians (23 December 1909 – 17 February 1934) and Commander-in-chief of the Belgian army
- Charles de Broqueville – Prime Minister (1912–1918); replaced by Gérard Cooreman in June 1918 shortly before the end of the war.
- Félix Wielemans – Chief of Staff of the Belgian Army
- Gérard Leman – general commanding the defense of Liège
- Théophile Figeys – general in the Hundred Days' Offensive
- Charles Tombeur – commander of the colonial Force Publique in the East African theater
فرنسا
- Raymond Poincaré – President of France
- René Viviani – Prime Minister of France (13 June 1914 – 29 October 1915)
- Aristide Briand – Prime Minister of France (29 October 1915 – 20 March 1917)
- Alexandre Ribot – Prime Minister of France (20 March 1917 – 12 September 1917)
- Paul Painlevé – Prime Minister of France (12 September 1917 – 16 November 1917)
- Georges Clemenceau – Prime Minister of France (From 16 November 1917)
- Divisional General / Marshal Joseph Joffre – Commander-in-Chief of the French Army (3 August 1914 – 13 December 1916)
- Divisional General Robert Nivelle – Commander-in-Chief of the French Army (13 December 1916 – April 1917)
- Divisional General / Marshal Philippe Pétain – Commander-in-Chief of the French Army (April 1917 – 11 November 1918)
- Divisional General / Marshal Ferdinand Foch – Supreme Allied Commander (26 March 1918 – 11 November 1918)
- Divisional General Maurice Sarrail – Commander of the Allied armies at Salonika Front (1915–1917)
- Army General Adolphe Guillaumat – Commander of the Allied armies at Salonika Front (1917–1918)
- Divisional General / Marshal Louis Franchet d'Espèrey – Commander of the Allied armies at Salonika Front (1918)
- Brigadier General Milan Rastislav Štefánik – General of French Army, Commander of Czechoslovak Legions
الامبراطورية البريطانية
- George V – King of the United Kingdom, Emperor of India
- H. H. Asquith – Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (Until 5 December 1916)
- David Lloyd George – Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (From 7 December 1916)
- Field Marshal Horatio Herbert Kitchener – Secretary of State for War (5 August 1914 – 5 June 1916)
- General William Robertson – Chief of the Imperial General Staff (23 December 1915 – February 1918)
- General Henry Wilson – Chief of the Imperial General Staff (February 1918 – February 1922)
- General John French – Commander-in-Chief of the British Expeditionary Force (4 August 1914 – 15 December 1915)
- General / Field Marshal Douglas Haig – Commander-in-Chief of the British Expeditionary Force (15 December 1915 – 11 November 1918)
- General Hugh Trenchard – Commander of Royal Flying Corps – (August 1915 – January 1918)
- Winston Churchill – First Lord of the Admiralty – (1911 – May 1915)
- Arthur Balfour- First Lord of the Admiralty – (May 1915 – December 1916)
- Edward Carson – First Lord of the Admiralty – (10 December 1916 – 17 July 1917)
- Eric Geddes – First Lord of the Admiralty – (July 1917 – January 1919)
- Admiral of the Fleet John "Jackie" Fisher – First Sea Lord – (1914 – May 1915)
- Admiral Henry Jackson – First Sea Lord – (May 1915 – November 1916)
- Admiral John Jellicoe – Commander of the Grand Fleet (August 1914 – November 1916); First Sea Lord (November 1916 – December 1917)
- Admiral Rosslyn Wemyss – First Sea Lord (December 1917 – November 1919)
- Admiral David Beatty – Commander of the Grand Fleet (November 1916 – April 1919)
- General Edmund Allenby – Commander of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (June 1917 – November 1918)
Dominion of Canada
- Robert Borden – Prime Minister of Canada (1914–18)
- Sam Hughes – Minister of Militia and Defence (1914 – January 1915)
- Joseph Flavelle- Chairman of Imperial Munitions Board (1915–19)
- General Julian Byng (June 1916 – June 1917) Canadian Corps commander
- Lieutenant-General Edwin Alderson – Commander of the unified Canadian Corps of the Canadian Expeditionary Force (26 January 1915 – September 1915)
- General Arthur Currie – Commander of the unified Canadian Corps of the Canadian Expeditionary Force (June 1917 –)[18]
كومنولث أستراليا
- Joseph Cook – Prime Minister of Australia (until 17 September 1914)
- Andrew Fisher – Prime Minister of Australia (17 September 1914 – 27 October 1915)
- Billy Hughes – Prime Minister of Australia (from 27 October 1915)
- General John Monash – Commander of the Australian Corps (all five Australian infantry divisions serving on the Western Front) (May 1918 –)
- Major General William Holmes – Commander of the Australian Naval and Military Expeditionary Force (August 1914 – February 1915)
- General Harry Chauvel – Commander of Desert Mounted Corps (Sinai and Palestine) (August 1917 –)
امبراطورية الهند
- Charles Hardinge, 1st Baron Hardinge of Penshurst – Viceroy of India 1910–1916
- Frederic Thesiger, 1st Viscount Chelmsford – Viceroy of India 1916–1921
- Austen Chamberlain – Secretary of State for India
- Lieutenant-General John Nixon commander of the British Indian Army (active in the Middle East)
اتحاد جنوب أفريقيا
- General Louis Botha – Prime Minister of South Africa
- General Jan Smuts – Led forces in South-West Africa Campaign and East African Campaign, later member of the Imperial War Cabinet
نيوزيلندا
- William Massey – Prime Minister of New Zealand
- General Sir Alexander Godley – Commandant of New Zealand Military Forces (to October 1914); Commander of the New Zealand Expeditionary Force
- Major General Sir Alfred William Robin – Quartermaster-General and Commandant of New Zealand Military Forces (from October 1914)
- Major General Sir Andrew Hamilton Russell – Commander of the New Zealand Division
دومنيون نيوفاوندلاند
- Sir Edward Morris – Prime Minister of Newfoundland (1909–1917)
- Sir John Crosbie – Prime Minister of Newfoundland (1917–1918)
- Sir William Lloyd – Prime Minister of Newfoundland (1918–1919)
اليابان
- Emperor Taishō – Emperor of Japan
- Ōkuma Shigenobu – Prime Minister of Japan (16 April 1914 – 9 October 1916)
- Terauchi Masatake – Prime minister of Japan (9 October 1916 – 29 September 1918)
- Hara Takashi – Prime minister of Japan (29 September 1918 – 4 November 1921)
- Kōzō Satō – Commander of the Second Special Task Fleet
- Kamio Mitsuomi – Commander of Allied land forces at Tsingtao
إيطاليا
- Victor Emmanuel III – King of Italy
- Antonio Salandra – Prime Minister (until 18 June 1916)
- Paolo Boselli – Prime Minister (18 June 1916 – 29 October 1917)
- Vittorio Emanuele Orlando – Prime Minister (from 29 October 1917)
- Luigi Cadorna – Commander-in-Chief of the Royal Italian Army
- Armando Diaz – Chief of General Staff of the Royal Italian army
- Luigi, Duke of Abruzzi – Commander-in-Chief of the Adriatic Fleet of Italy (1914–17)
- Paolo Thaon di Revel – Admiral of the Royal Italian Navy
رومانيا
- Ferdinand I – King of Romania
- General Constantin Prezan – Chief of the General Staff of Romania
- Ion I. C. Brătianu – Prime Minister of Romania
- Vintilă Brătianu – Secretary of War
- Field Marshal Alexandru Averescu – Commander of the 2nd Army, 3rd Army, then Army Group South
- General Eremia Grigorescu – Commander of the 1st Army
اليونان
- Eleftherios Venizelos: Prime minister of Greece after 13 June 1917.
- Constantin I: King of Greece, he retired from the throne, without formally resigning.
- George: Crown Prince of Greece, designated King after his father retired form the throne, he refused to become the new king and followed his father in exile.
- Alexander: King of Greece, he became King of Greece after his father and brother retired from the throne.
- Panagiotis Danglis: Greek general in the Hellenic Army.
الولايات المتحدة
- Woodrow Wilson – President of the United States/Commander-In-Chief of the U.S. armed forces
- Newton D. Baker – U.S. Secretary of War
- Josephus Daniels – United States Secretary of the Navy
- Major General / General John J. Pershing – Commander of the American Expeditionary Force
- Rear Admiral / Vice Admiral William Sims – Commander of U.S. Naval Forces in European Waters
- Brigadier General Mason Patrick – Commander of the United States Army Air Service
البرتغال
- Bernardino Machado – President of Portugal (until 12 December 1917)
- Afonso Costa – Prime Minister of Portugal (until 15 March 1916; then again 25 April 1917 – 10 December 1917)
- António José de Almeida – Prime Minister of Portugal (15 March 1916 – 25 April 1917)
- Sidónio Pais – Prime Minister of Portugal and War Minister (11 December 1917 – 9 May 1918) and رئيس البرتغال (from 9 May 1918)
- José Norton de Matos – War Minister (until 10 December 1917)
- João Tamagnini Barbosa – Interim War Minister (9 May 1918 – 15 May 1918)
- Amílcar Mota – Secretary of State for War (15 May 1918 – 8 October 1918)
- Álvaro de Mendonça – Secretary of State for War (from 8 October 1918)
- Fernando Tamagnini de Abreu – قائد Portuguese Expeditionary Corps (CEP)
- José Augusto Alves Roçadas – Commander of the Portuguese Forces in Southern Angola
- José Luís de Moura Mendes – Commander of the Portuguese Forces in Eastern Africa (حتى يونيو 1916)
- José César Ferreira Gil – Commander of the Portuguese Forces in Eastern Africa (from June 1916)
- Sousa Rosa – Commander of the Portuguese Forces in Eastern Africa (من 1917)
سيام (تايلند)
انظر المقال الرئيسي: سيام في الحرب العالمية الأولى
- Vajiravudh – ملك سيام
- Chakrabongse Bhuvanath – قائد Siamese Expeditionary Forces in الجبهة الغربية.
- General Phya Pijaijarnrit – Supreme Commander Siamese Expeditionary Forces in الحرب العالمية الأولى
البرازيل
See main Article: Brazil during World War I
- Venceslau Brás – President of Brazil
- Admiral Pedro Frontin, Chief of DNOG (Brazilian Expeditionary Fleet)
- General Napoleão Felipe Aché, Chief of Brazilian Military Mission in France (1918–1919)
- M.D. Nabuco Gouveia – Chief of Brazilian Military Medical Commission
الأفراد والخسائر
These are estimates of the cumulative number of different personnel in uniform 1914–1918, including army, navy and auxiliary forces. At any one time, the various forces were much smaller. Only a fraction of them were frontline combat troops. The numbers do not reflect the length of time each country was involved. (See also: World War I casualties.)
| Allied power | Mobilized personnel | Military Fatalities | Wounded in action | Total casualties | Casualties as % of total mobilized |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | 412,953[48] | 61,928[19] | 152,171 | 214,099 | 52% |
| Belgium | 267,000[49] | 38,172[20] | 44,686 | 82,858 | 31% |
| Canada | 628,964[50] | 64,944[21] | 149,732 | 214,676 | 34% |
| France | 8,410,000[51] | 1,397,800[22] | 4,266,000 | 5,663,800 | 67% |
| Greece | 230,000[52] | 26,000[23] | 21,000 | 47,000 | 20% |
| India | 1,440,437[53] | 74,187[24] | 69,214 | 143,401 | 10% |
| Italy | 5,615,000[54] | 651,010[25] | 953,886 | 1,604,896 | 29% |
| Japan | 800,000[55] | 415[26] | 907 | 1,322 | <1% |
| Monaco | 80[27] | 8[27] | 0 | 8[27] | 10% |
| Montenegro | 50,000[56] | 3,000 | 10,000 | 13,000 | 26% |
| Nepal | 200,000[28] | 30,670 | 21,009 | 49,823 | 25% |
| New Zealand | 128,525[57] | 18,050[29] | 41,317 | 59,367 | 46% |
| Portugal | 100,000[58] | 7,222[30] | 13,751 | 20,973 | 21% |
| Romania | 750,000[59] | 250,000[31] | 120,000 | 370,000 | 49% |
| Russia | 12,000,000[60] | 1,811,000[32] | 4,950,000 | 6,761,000 | 56% |
| Serbia | 707,343[61] | 275,000[33] | 133,148 | 408,148 | 58% |
| Siam | 1,284[62] | 19 | 0 | 19 | 2% |
| South Africa | 136,070[63] | 9,463[34] | 12,029 | 21,492 | 16% |
| United Kingdom | 6,211,922[64] | 886,342[35] | 1,665,749 | 2,552,091 | 41% |
| United States | 4,355,000[65] | 116,708[36] | 205,690 | 322,398 | 7% |
| Total | 42,244,409 | 5,741,389 | 12,925,833 | 18,744,547 | 49% |
ملخص إعلانات الحرب
| التاريخ | المعلِن | على |
|---|---|---|
| 1914 | ||
| 28 يوليو | Austria-Hungary | Serbia |
| 30 July | Russia | Austria-Hungary |
| 1 August | Germany | Russia |
| 3 August | Germany | France |
| 4 August | Germany | Belgium |
| United Kingdom | Germany | |
| 5 August | Montenegro | Austria-Hungary |
| 6 August | Austria-Hungary | Russia |
| Serbia | Germany | |
| 9 August | Montenegro | Germany |
| 11 August | France | Austria-Hungary |
| 12 August | United Kingdom | Austria-Hungary |
| 22 August | Austria-Hungary | Belgium |
| 23 August | Japan | Germany |
| 25 August | Japan | Austria-Hungary |
| 1 November | Russia | Ottoman Empire |
| 2 November | Serbia | Ottoman Empire |
| 3 November | Montenegro | Ottoman Empire |
| 5 November | United Kingdom France |
Ottoman Empire |
| 1915 | ||
| 23 May | Italy | Austria-Hungary |
| 3 June | San Marino | Austria-Hungary |
| 21 August | Italy | Ottoman Empire |
| 14 October | Bulgaria | Serbia |
| 15 October | United Kingdom Montenegro |
Bulgaria |
| 16 October | France | Bulgaria |
| 19 October | Italy Russia |
Bulgaria |
| 1916 | ||
| 9 March | Germany | Portugal |
| 15 March | Austria-Hungary | Portugal |
| 27 August | Romania | Austria-Hungary |
| Italy | Germany | |
| 28 August | Germany | Romania |
| 30 August | Ottoman Empire | Romania |
| 1 September | Bulgaria | Romania |
| 1917 | ||
| 6 April | United States | Germany |
| 7 April | Cuba | Germany |
| 10 April | Bulgaria | United States |
| 13 April | Bolivia | Germany |
| 20 April | Ottoman Empire | United States |
| 2 July | Greece | Germany Austria-Hungary Ottoman Empire Bulgaria |
| 22 July | Siam | Germany Austria-Hungary |
| 4 August | Liberia | Germany |
| 14 August | China | Germany Austria-Hungary |
| 6 October | Peru | Germany |
| 7 October | Uruguay | Germany |
| 26 October | Brazil | Germany[37] |
| 7 December | United States | Austria-Hungary |
| 7 December | Ecuador | Germany |
| 10 December | Panama | Austria-Hungary |
| 16 December | Cuba | Austria-Hungary |
| 1918 | ||
| 23 April | Guatemala | Germany |
| 8 May | Nicaragua | Germany Austria-Hungary |
| 23 May | Costa Rica | Germany |
| 12 July | Haiti | Germany |
| 19 July | Honduras | Germany |
| 10 November | Romania | Germany |
انظر أيضاً
الهامش
- ^ Karel Schelle, The First World War and the Paris Peace Agreement, GRIN Verlag, 2009, p. 24
- ^ First World War.com – Feature Articles – The Causes of World War One
- ^ The Treaty of Sèvres, 1920
- ^ US Declaration of War
- ^ Declarations of War and Authorizations for the Use of Military Force: Historical Background and Legal Implications
- ^ H.J.Res.169: Declaration of War with Austria-Hungary, WWI, United States Senate
- ^ Tucker&Roberts pp. 1232, 1264
- ^ Tucker&Roberts p. 1559
- ^ Perry (2004), p.xiii
- ^ S.N. Broadberry; Mark Harrison (2005). The Economics of World War I. illustrated. Cambridge University Press. p. 7. Retrieved 2015-03-16.
- ^ Korea, Formosa, Kwantung and Sakhalin
- ^ Serbia, Montenegro and Bosnia-Hercegovina
- ^ As Hawaii and Alaska were not yet U.S. states, they are included in the dependencies
- ^ Costa Rica, Cuba, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Nicaragua and Panama
- ^ S.N. Broadberry; Mark Harrison (2005). The Economics of World War I. illustrated. Cambridge University Press. p. 8. Retrieved 2015-03-16.
- ^ Germany (and colonies), Austria-Hungary, Ottoman Empire and Bulgaria
- ^ Abdullah I of Jordan; Philip Perceval Graves (1950). Memoirs. p. 186.
- ^ first Canadian to attain the rank of full general
- ^ Australia casualties
Included in total are 55,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[1]-.
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.[2]-
Totals include 2,005 military deaths during 1919–21[3]-. The 1922 War Office report listed 59,330 Army war dead[4]. - ^ Belgium casualties
Included in total are 35,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[5] Figures include 13,716 killed and 24,456 missing up until Nov.11, 1918. "These figures are approximate only, the records being incomplete." [6]. - ^ Canada casualties
Included in total are 53,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds.[7]
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.[8]
Totals include 3,789 military deaths during 1919–21 and 150 Merchant Navy deaths[9]-. The losses of Newfoundland are listed separately on this table. The 1922 War Office report listed 56,639 Army war dead[10]. - ^ France casualties
Included in total are 1,186,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[11]. Totals include the deaths of 71,100 French colonial troops. [12]-Figures include war related military deaths of 28,600 from 11/11/1918 to 6/1/1919.[13] - ^ Greece casualties
Jean Bujac in a campaign history of the Greek Army in World War One listed 8,365 combat related deaths and 3,255 missing[14], The Soviet researcher Boris Urlanis estimated total dead of 26,000 including 15,000 military deaths due disease[15] - ^ India casualties
British India included present-day India, Pakistan and Bangladesh.
Included in total are 27,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[16].
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.[17]
Totals include 15,069 military deaths during 1919–21 and 1,841 Canadian Merchant Navy dead[18]. The 1922 War Office report listed 64,454 Army war dead[19] - ^ Italy casualties
Included in total are 433,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[20]
Figures of total military dead are from a 1925 Italian report using official data[21]. - ^ War dead figure is from a 1991 history of the Japanese Army[22].
- ^ أ ب ت Monaco 11-Novembre : ces Monégasques morts au champ d'honneur | Nice-Matin
- ^ Jain, G (1954) India Meets China in Nepal, Asia Publishing House, Bombay P92
- ^ New Zealand casualties
Included in total are 14,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[23].
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.[24]
Totals include 702 military deaths during 1919–21[25]. The 1922 War Office report listed 16,711 Army war dead[26]. - ^ Portugal casualties
Figures include the following killed and died of other causes up until Jan.1, 1920; 1,689 in France and 5,332 in Africa. Figures do not include an additional 12,318 listed as missing and POW[27]. - ^ Romania casualties
Military dead is "The figure reported by the Rumanian Government in reply to a questionnaire from the International Labour Office"[28]. Included in total are 177,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[29]. - ^ Russia casualties
Included in total are 1,451,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[30]. The estimate of total Russian military losses was made by the Soviet researcher Boris Urlanis.[31] - ^ Serbia casualties
Included in total are 165,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[32].The estimate of total combined Serbian and Montenegrin military losses of 278,000 was made by the Soviet researcher Boris Urlanis[33]
- ^ South Africa casualties
Included in total are 5,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[34]
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.[35]
Totals include 380 military deaths during 1919–21[36]. The 1922 War Office report listed 7,121 Army war dead[37]. - ^ UK and Crown Colonies casualties
Included in total are 624,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[38].
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.[39]
Military dead total includes 34,663 deaths during 1919–21 and 13,632 British Merchant Navy deaths[40]. The 1922 War Office report listed 702,410 war dead for the UK[41], 507 from "Other colonies"[42] and the Royal Navy (32,287)[43].
The British Merchant Navy losses of 14,661 were listed separately [44]; The 1922 War Office report detailed the deaths of 310 military personnel due to air and sea bombardment of the UK[45]. - ^ United States casualties
Official military war deaths listed by the US Dept. of Defense for the period ending Dec. 31, 1918 are 116,516; which includes 53,402 battle deaths and 63,114 other deaths.[46], The US Coast Guard lost an additional 192 dead [47]. - ^ Declarations of War, 1914–1918
مراجع
- ^1 The War Office (2006) [1922]. Statistics of the military effort of the British Empire during the Great War 1914—1920. Uckfield, East Sussex: Military and Naval Press. ISBN 1-84734-681-2. OCLC 137236769.
- ^2 Gilbert Martin (1994). Atlas of World War I. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-521077-8. OCLC 233987354.
- ^3 Tucker Spencer C (1999). The European Powers in the First World War: An Encyclopedia. New York: Garland. ISBN 0-8153-3351-X.
- ^4 The Commonwealth War Graves Commission. "Annual Report 2005-2006" (PDF).
- ^5 The Commonwealth War Graves Commission. "Debt of Honour Register".
- ^6 Urlanis Boris (2003) [1971, Moscow]. Wars and Population. Honolulu: University Press of the Pacific. OCLC 123124938.
- ^7 Huber Michel (1931). La population de la France pendant la guerre, avec un appendice sur Les revenus avant et après la guerre (in French). Paris. OCLC 4226464.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^8 Bujac Jean Léopold Emile (1930). Les campagnes de l'armèe Hellènique 1918–1922 (in French). Paris: Charles-Lavauzelle. OCLC 10808602.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^9 Mortara Giorgio (1925). La Salute pubblica in Italia durante e dopo la Guerra (in Italian). New Haven, Connecticut: Yale University Press. OCLC 2099099.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^10 Harries Merion, Harries Susie (1991). Soldiers of the Sun – The Rise and Fall of the Imperial Japanese Army. Random House. ISBN 0-679-75303-6. OCLC 32615324.
- ^11 Clodfelter Michael (2002). Warfare and Armed Conflicts : A Statistical Reference to Casualty and Other Figures, 1500–2000 (2nd ed.). London: McFarland. ISBN 0-7864-1204-6. OCLC 48066096.
المصادر
انظر قائمة كتب الحرب العالمية الأولى
- Ellis, John and Mike Cox. The World War I Databook: The Essential Facts and Figures for All the Combatants (2002)
- Esposito, Vincent J. The West Point Atlas of American Wars: 1900–1918 (1997) despite the title covers entire war; online maps from this atlas
- Falls, Cyril. The Great War (1960), general military history
- Higham, Robin and Dennis E. Showalter, eds. Researching World War I: A Handbook (2003), historiography, stressing military themes
- Pope, Stephen and Wheal, Elizabeth-Anne, eds. The Macmillan Dictionary of the First World War (1995)
- Strachan, Hew. The First World War: Volume I: To Arms (2004)
- Trask, David F. The United States in the Supreme War Council: American War Aims and Inter-Allied Strategy, 1917–1918 (1961)
- Tucker, Spencer, ed. The Encyclopedia of World War I: A Political, Social, and Military History (5 volumes) (2005), online at eBook.com
- Tucker, Spencer, ed. European Powers in the First World War: An Encyclopedia (1999)