ميتاسيليكات الصوديوم
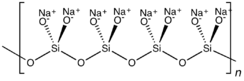
ميتاسيليكات الصوديوم هي مركب كيميائي بصيغة Na 2SiO 3، التي هي المركب الرئيسي في محاليل سليكات الصوديوم التجارية. وهي مركب أيوني يتكون من كاتيونات الصوديوم Na+ وأنيونات الميتاسيليكات الپوليمرية [–SiO2−3–]n. وهي مادة صلبة بلورية عديمة اللون مُرَطـِّبة ومُذوِّبة، تذوب في الماء (معطيةً محلولاً قلوياً) ولكن لا تذوب في الكحولات.[1]
| |
| |

| |
| الأسماء | |
|---|---|
| اسم أيوپاك
Sodium metasilicate
| |
| Identifiers | |
| رقم CAS | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| اختصارات | E550 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.027.193 |
| رقم EC |
|
| عناوين مواضيع طبية MeSH | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| رقم RTECS |
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | 1759 3253 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| InChI | InChI={{{value}}} |
| SMILES | |
| الخصائص | |
| الصيغة الجزيئية | Na2O3Si |
| كتلة مولية | 122.05 g mol-1 |
| المظهر | White crystals |
| الكثافة | 2.61 g/cm3 |
| نقطة الانصهار | |
| قابلية الذوبان في الماء | 22.2 g/100 ml (25 °C) 160.6 g/100 ml (80 °C) |
| قابلية الذوبان | insoluble in alcohol |
| معامل الانكسار (nD) | 1.52 |
| الكيمياء الحرارية | |
| الإنتالپية المعيارية للتشكل ΔfH |
−1561.43 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy S |
113.71 J/(K·mol) |
| سعة الحرارة النوعية، C | 111.8 J/(K·mol) |
| المخاطر | |
| صفحة بيانات السلامة | Avantor Performance Materials |
| ن.م.ع. مخطط تصويري |  
|
| ن.م.ع. كلمة الاشارة | Danger |
| H302, H314, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (معيـَّن النار) | |
| الجرعة أو التركيز القاتل (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (الجرعة الوسطى)
|
1153[مطلوب توضيح] (rat, oral) |
| مركبات ذا علاقة | |
أنيونات أخرى
|
كربونات الصوديوم جرمانات الصوديوم ستانات الصوديوم بلومبيت الصوديوم |
كاتيونات أخرى
|
سيليكات البوتاسيوم |
ما لم يُذكر غير ذلك، البيانات المعطاة للمواد في حالاتهم العيارية (عند 25 °س [77 °ف]، 100 kPa). | |
| مراجع الجدول | |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
التحضير والخصائص
The anhydrous compound can be prepared by fusing silicon dioxide SiO 2 (silica, quartz) with sodium oxide Na 2O in 1:1 molar ratio.[2]
The compound crystallizes from solution as various hydrates, such as
- pentahydrate Na 2SiO 3·5H 2O (CAS 10213-79-3, EC 229-912-9, PubChem 57652358)
- nonahydrate Na 2SiO 3·9H 2O (CAS 13517-24-3, EC 229-912-9, PubChem 57654617)[3]
البنية
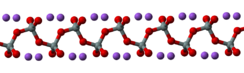
In the anhydrous solid, the metasilicate anion is actually polymeric, consisting of corner-shared {SiO4} tetrahedra, and not a discrete SiO32− ion.[4]
In addition to the anhydrous form, there are hydrates with the formula Na2SiO3·nH2O (where n = 5, 6, 8, 9), which contain the discrete, approximately tetrahedral anion SiO2(OH)22− with water of hydration. For example, the commercially available sodium silicate pentahydrate Na2SiO3·5H2O is formulated as Na2SiO2(OH)2·4H2O, and the nonahydrate Na2SiO3·9H2O is formulated as Na2SiO2(OH)2·8H2O.[5] The pentahydrate and nonahydrate forms have their own CAS Numbers, 10213-79-3 and 13517-24-3 respectively.
الاستخدامات
تتفاعل ميتاسيليكات الصوديوم مع الأحماض لانتاج هلام السيليكا.[6]
- Cements and Binders - dehydrated sodium metasilicate forms cement or binding agent.
- Pulp and Par - sizing agent and buffer/stabilizing agent when mixed with hydrogen peroxide.
- Soaps and Detergents - as an emulsifying and suspension agent.
- Automotive applications - decommissioning of old engines (CARS program), cooling system sealant, exhaust repair.
- Egg Preservative - seals eggs increasing shelf life.
- Crafts - forms "stalagmites" by reacting with and precipitating metal ions. Also used as a glue called "soluble glass".
- Hair coloring kits
ويُستخدم الزجاج المائيّ في المواد المنظفة، وفي الصابون وفي صيانة الخشب، وفي الخشب المقاوم للنار، والقماش والورق. والمحلول يجعل الجدران مقاومة للماء، ويُستخدم مادة لاصقة في صنع صناديق الشحن ذات الألواح الليمفاوية والصناديق الصامدة للشحم والحاويات المماثلة. كما يستخدم أيضًا في صنع الإسمنت وفي تقوية الخرسانة، ويُستخدم الزجاج المائي في تنقية الدهون والزيوت، وفي تكرير النفط وفي صنع جل السليكا (وهو نوع من السليكا شديد الامتصاص) كما يُستخدم في صنع المواد الحفازة (وهي مواد تعمل على سرعة التفاعلات الكيميائية).
انظر أيضاً
المصادر
- ^ Chemical Book: "Sodium metasilicate". Accessed on 2018-05-13.
- ^ J. F. Schairer and N. L. Bowen (1956): "The system Na 2O—Al 2O 3—SiO 2". American Journal of Science, volume 254, issue 3, pages 129-195 DOI:10.2475/ajs.254.3.129
- ^ M. F. Bechtold (1955): "Polymerization and Properties of Dilute Aqueous Silicic Acid from Cation Exchange" Journal of Physical Chemistry, volume 59, issue 6, pages 532–541. DOI:10.1021/j150528a013
- ^ Greenwood, N. N. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edition ed.). Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-7506-3365-4.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Wells A.F. (1984) Structural Inorganic Chemistry 5th edition Oxford Science Publications ISBN 0-19-855370-6
- ^ "Uses of Sodium Metasilicate".
