قوات الحلفاء (الحرب العالمية الأولى)
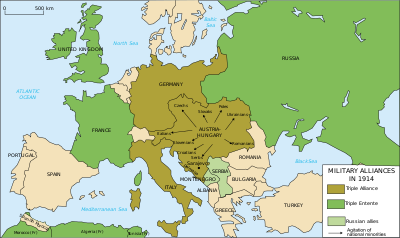
قوى الوفاق (الحلفاء) في فترة الحرب العالميّة الأولى (1914 – 1918م ) الدّول التاليّة: بريطانيا ، فرنسا ، روسيا .
Allies of World War I Entente Powers | |
|---|---|
| 1914–1918 | |
| |
| المكانة | Military alliance |
| الحقبة التاريخية | World War I |
• تأسست | 1914 |
• Disestablished | 1918 |
ضمت مجموعة (المحور ، الدّول التاليّة: ألمانيا ، الإمبراطوريّة النمساويّة المجريّة، تركيا.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
التاريخ
اتخذ المجتمع الدولي إجراءات عقابيّة ضد ألمانيا فيما عرف بمعاهدة ڤرساي 1919م، وذلك بعد انتهاء الحرب العالميّة الأولى. خسرت ألمانيا بموجب تلك الإجراءات العقابيّة (معاهدة فرساي ) كما جاء في مصادر التوثيق الدوليّة: 12,5% من مساحتها الجغرافيّة، وحوالي 12% من تعداد سكانها، وما يقارب عن 15% من إنتاجها الزراعي، وحوالي 10% من منتوجها الصناعي وما يقارب عن 75% من إنتاجها من خام الحديد. وإلى جانب ذلك، قيدت معاهدة فرساي حركة وصلاحيات الجيش الألماني حيث نصت على ألا يزيد عدد المنتسبين إلى الجيش الألماني عن مائة ألف جندي، كذلك، ألزمت ألمانيا بدفع تعويضات كبيرة للحلفاء.
The direction of the war changed on April 6, 1917, with the entrance of the الولايات المتحدة and its American allies.[بحاجة لمصدر] Liberia, China, Siam and Greece also became allies. After the October Revolution, Russia left the alliance and ended formal involvement in the war, by the signing of the treaty of Brest Litovsk in November effectively creating a separate peace with the Central Powers. This was followed by Romanian cessation of hostilities, however the Balkan State declared war on Central Powers again on November 10, 1918. The Russian withdrawal allowed for the final structure of the alliance, which was based on five Great Powers:
| التعداد | المساحة | GDP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Russian Empire (plus Finland), 1914 | 173.2m (176.4m) | 21.7m km2 (22.1m km2) | $257.7b ($264.3b) |
| French Third Republic (plus colonies), 1914 | 39.8m (88.1m) | 0.5m كم2 (11.2m km2) | $138.7b ($170.2b) |
| United Kingdom (plus colonies and Dominions), 1914 | 46.0m (446.1m) | 0.3m كم2 (33.3m km2) | $226.4b ($561.2b) |
| امبراطورية اليابان (plus colonies), 1914 | 55.1m (74.2m) | 0.4m km2 (0.7m km2) | $76.5b ($92.8b) |
| Kingdom of Italy (plus colonies), 1915 | 35.6m (37.6m) | 0.3m km2 (2.3m 2 ) | $91.3b ($92.6b) |
| الولايات المتحدة (plus overseas dependencies),[2] 1917 | 96.5m (106.3m) | 7.8m km2 (9.6m km2) | $511.6b ($522.2b) |
| Allied approximate Total by 1917 | 928.7m | 79.2m km2 | $1,703.3b |
الزعماء
المملكة المتحدة/الامبراطورية البريطانية
- George V - King of the United Kingdom, Emperor of India
- H. H. Asquith - Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (Until 5 December 1916)
- D. Lloyd George - Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (From 7 December 1916)
- Horatio Herbert Kitchener - Secretary of State for War (5 August 1914 – 5 June 1916)
- William Robertson - Chief of the Imperial General Staff
- John French - Commander-in-Chief of the British Expeditionary Force (4 August 1914 – 15 December 1915)
- Douglas Haig - Commander-in-Chief of the British Expeditionary Force (15 December 1915 – 11 November 1918)
- Hugh Trenchard, 1st Viscount Trenchard - Commander of Royal Flying Corps - (August 1915 – January 1918)
- Winston Churchill - First Lord of the Admiralty - (1911 – May 1915)
- Arthur Balfour- First Lord of the Admiralty - (May 1915 – December 1916)
- Edward Carson - First Lord of the Admiralty - (10 December 1916 – 17 July 1917)
- Eric Geddes - First Lord of the Admiralty - (July 1917 – January 1919)
- "Jackie" Fisher - First Sea Lord - (1914 – May 1915)
- Henry Jackson - First Sea Lord - (May 1915 – November 1916)
- John Jellicoe - First Sea Lord (November 1916 – December 1917)
- Rosslyn Wemyss - First Sea Lord (December 1917 – November 1919)
دومنيون كندا
- Robert Borden - Prime Minister of Canada (1914–18)
- Sam Hughes- Minister of Militia and Defence (1914 – January 1915)
- Joseph Flavelle- Chairmen of Imperial Munitions Board (1915–19)
- Julian Byng (June 1916 – June 1917) Canadian Corps commander
- Edwin Alderson - Commander of the unified Canadian Corps of the Canadian Expeditionary Force (26 January 1915 – September 1915)
- Arthur Currie - Commander of the unified Canadian Corps of the Canadian Expeditionary Force (June 1917 –)[3]
كومنولث أستراليا
- Andrew Fisher - رئيس وزراء أستراليا (until 27 October 1915)
- Billy Hughes - Prime Minister of Australia (from 27 October 1915)
- John Monash - Commander of the Australian Corps (all five Australian infantry divisions serving on the Western Front) (May 1918 –)
الامبراطورية الهندية
- John Nixon commander of the British Indian Army (active in the Middle East)
اتحاد جنوب أفريقيا
- Louis Botha - Prime Minister of South Africa
- Jan Smuts - Led forces in South-West Africa Campaign and East African Campaign, later member of the Imperial War Cabinet
روسيا
- Nicholas II — Russian Emperor, King of Poland, and Grand Prince of Finland. (Until 15 March 1917)
- Grand Duke Nicholas Nikolaevich - Commander-in-chief (1 August 1914 – 5 September 1916) and viceroy in the Caucasus
- Alexander Samsonov - Commander of the Russian Second Army for the invasion of East Prussia (1 August 1914 – 29 August 1914)
- Paul von Rennenkampf - Commander of the Russian First Army for the invasion of East Prussia (1 August 1914 – November 1914)
- Nikolai Ivanov - Commander of the Russian army on the Southwestern Front, (1 August 1914 – March 1916) responsible for much of the action in Galicia
- Aleksei Brusilov - Commander of the South-West Front, then provisional Commander-in-Chief after the Tsar's abdication (February 1917 – August 1917)
- Lavr Georgievich Kornilov - Commander of the South-West Front, then Commander-in-Chief (August 1917)
- Aleksey Kuropatkin - Commander of the Northern Front (October 1915 – 1917)
- Nikolai Yudenich - Commander of the Caucasus (January 1915 – May 1917)
- Andrei Eberhardt - Commander of Black Sea Fleet (1914–16)
- Aleksandr Kolchak - Commander of Black Sea Fleet (1916–17)
- Nikolai Essen - Commander of Baltic Fleet (1913 – May 1915)
فرنسا
- Raymond Poincaré - President of France
- René Viviani - Prime Minister of France (13 June 1914 – 29 October 1915)
- Aristide Briand - Prime Minister of France (29 October 1915 – 20 March 1917)
- Alexandre Ribot - Prime Minister of France (20 March 1917 – 12 September 1917)
- Paul Painlevé - Prime Minister of France (1GHGH2 September 1917 – 16 November 1917)
- Georges Clemenceau - Prime Minister of France (From 16 November 1917)
- Joseph Joffre - Commander-in-Chief of the French Army (3 August 1914 – 13 December 1916) and Marshal of France
- Robert Nivelle - Commander-in-Chief of the French Army (13 December 1916 – April 1917)
- Philippe Pétain - Commander-in-Chief of the French Army (April 1917 – 26 March 1918) and Marshal of France
- Ferdinand Foch - Commander-in-Chief of the French Army and Marshal of France, Supreme Allied Commander (26 March 1918 – 11 November 1918)
- Milan Rastislav Stefanik - General of French Army, Commander of Czechoslovak Legions
- Georges Thenault - Commander of the Lafayette Escadrille
صربيا
- Peter I - King of Serbia
- Vojvoda Radomir Putnik - Chief of the General Staff of the Serbian Army
- Vojvoda Petar Bojović - Commander of First Army, later Chief of General Staff
- Vojvoda Stepa Stepanović - Commander of Second Army
- Vojvoda Živojin Mišić - Commander of 1st Serbian Army
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
الجبل الأسود
- Nicholas I - King of Montenegro
- Serdar Janko Vukotić - Commander of 1st Montenegrin Army
بلجيكا
- Albert I of Belgium - King of Belgium (23 December 1909 – 17 February 1934)
إيطاليا
- Victor Emmanuel III - King of Italy
- Antonio Salandra - Prime Minister (until June 18, 1916)
- Paolo Boselli - Prime Minister (June 18, 1916 – October 29, 1917)
- Vittorio Emanuele Orlando - Prime Minister (from October 29, 1917)
- Luigi Cadorna - Commander-in-Chief of the Italian army
- Armando Diaz - Chief of General Staff of the Italian army
- Luigi, Duke of Abruzzi - Commander-in-Chief of the Adriatic Fleet of Italy (1914–17)
- Paolo Thaon di Revel - Admiral of the Royal Italian Navy
- Vito Bolzanello da Roma- Captain of the Italian Navy
رومانيا
- Ferdinand I - King of Romania
- Constantin Prezan - Chief of the General Staff of Romania
- Alexandru Averescu - Commander of the Romanian 2nd Army, 3rd Army, then Army Group South
الولايات المتحدة
- Woodrow Wilson - رئيس الولايات المتحدة/Commander-In-Chief of the U.S. armed forces
- Newton D. Baker - U.S. Secretary of War
- John J. Pershing - Commander of the American Expeditionary Force
اليابان
- Emperor Taishō - Emperor of Japan
- Ōkuma Shigenobu - Prime Minister of Japan (16 April 1914 – 9 October 1916)
- Terauchi Masatake - Prime minister of Japan (9 October 1916 – 29 September 1918)
البرازيل
- Venceslau Bras - President of Brazil
- Pedro Frontin - Brazilian Admiral
- Dr. Nabuco Gouveia - Chief of the Brazilian Medical Delegation
البرتغال
- Bernardino Machado - President of Portugal
- Afonso Costa - Prime Minister of Portugal
- Norton de Matos -War Minister
- Tamagnini de Abreu - Commander of the Portuguese Expeditionary Corps (CEP)
- Alves Roçadas - Commander of the Portuguese Forces in Southern Angola
- Ferreira Gil - Commander of the Portuguese Forces in Eastern Africa
الصين
- Feng Guozhang - President of the Republic of China
- Duan Qirui - Premier of China
العديد والخسائر
| قوى الحلفاء | الحشود | قتلى الوغى | جرحى الوغى | إجمالي الخسائر | الخسائر كنسبة من إجمالي الحشود |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| أستراليا | 412,953[48] | 61,928[4] | 152,171 | 214,099 | 52% |
| بلجيكا | 267,000[49] | 38,172[5] | 44,686 | 82,858 | 31% |
| كندا | 628,964[50] | 64,944[6] | 149,732 | 214,676 | 34% |
| فرنسا | 8,410,000[51] | 1,397,800[7] | 4,266,000 | 5,663,800 | 67% |
| اليونان | 230,000[52] | 26,000[8] | 21,000 | 47,000 | 20% |
| الهند | 1,440,437[53] | 74,187[9] | 69,214 | 143,401 | 10% |
| إيطاليا | 5,615,000[54] | 651,010[10] | 953,886 | 1,604,896 | 29% |
| اليابان | 800,000[55] | 415[11] | 907 | 1,322 | <1% |
| الجبل الأسود | 50,000[56] | 3,000 | 10,000 | 13,000 | 26% |
| نـِپال | 200,000 | 30,000 | ? | ? | ? |
| نيوزيلندا | 128,525[57] | 18,050[12] | 41,317 | 59,367 | 46% |
| البرتغال | 100,000[58] | 7,222[13] | 13,751 | 20,973 | 21% |
| رومانيا | 750,000[59] | 250,000[14] | 120,000 | 370,000 | 49% |
| روسيا | 12,000,000[60] | 1,811,000[15] | 4,950,000 | 6,761,000 | 56% |
| صربيا | 707,343[61] | 275,000[16] | 133,148 | 408,148 | 58% |
| جنوب أفريقيا | 136,070[62] | 9,463[17] | 12,029 | 21,492 | 16% |
| المملكة المتحدة | 6,211,922[63] | 886,342[18] | 1,665,749 | 2,552,091 | 41% |
| الولايات المتحدة | 4,355,000[64] | 116,708[19] | 205,690 | 322,398 | 7% |
| الإجمالي | 42,243,214 | 5,691,241 | 12,809,280 | 18,500,521 | 44% |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ملخص إعلانات الحرب من قِبل الحلفاء على القوى المركزية
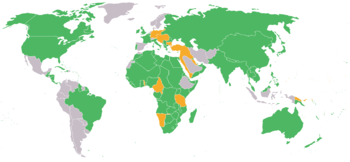
List of the 23 member States of the Entente:
بعد اغتيال فرانتس فرديناند
- مملكة صربيا: 28 July 1914
- الإمبراطورية الروسية: 1 August 1914 (separate peace in November 1917)
- France: 3 August 1914
- بلجيكا: 4 August 1914
- الامبراطورية البريطانية 4 August 1914
- نيپال 4 August 1914
- مملكة الجبل الأسود: 8 August 1914 (capitulation in January 1916)
- إمبراطورية اليابان: 23 August 1914
بعد معجزة المارن
- مملكة إيطاليا: 23 May 1915
- Portugal: 9 March 1916
- مملكة رومانيا: 27 August 1916 (capitulation in December 1917, returned in November 1918)
بعد الثورة الروسية
- United States: 6 April 1917
- Greece: Officially, 2 July 1917 (since 24 November 1916 by Movement of National Defence)
- Brazil: 26 October 1917
حالة خاصة: الامبراطورية البريطانية
Six Dominions of the British Empire, which were subordinate to London under international law, were admitted to the Conference of Versailles in recognition of their huge military involvement:
حالة خاصة: حلفاء إسمياً
Countries that declared war on Central Powers but had no military involvement in the conflict:
- كوبا: 8 April 1917
- پنما: 9 April 1917
- Siam: 22 July 1917
- ليبريا: 4 August 1917
- تايوان: 14 August 1917
- گواتيمالا: 25 April 1918
- نيكاراگوا: 7 May 1918
- كوستاريكا: 25 May 1918
- هندوراس: 19 July 1918
- هايتي: 25 July 1918
- أندورا: remained in an official state of belligerency until 1957 as it was not included in the Treaty of Versailles.[21]
Countries that severed relationships with Central Powers but did not declare war and had no military involvement:
حالة خاصة: قوميات ثائرة
Four insurgent nationalities, which voluntarily fought with the Allies and seceded from the constituent states of the Central Powers at the end of the war, were allowed to participate as winning nations to the peace treaties:
- Poles
- Czechoslovak Legions: armed by France, Italy and Russia
- مملكة الحجاز: armed by Britain in Arabia
- Armenians: seceded from Russia and fought against Ottoman Empire (many ethnic Armenians living in the Ottoman Empire fought for the Ottoman Empire until the Ottomans turned on them)
انظر أيضاً
الهامش
- ^ S.N. Broadberry, Mark Harrison. The Economics of World War I. illustrated ed. Cambridge University Press, 2005, pgs. 7-8.
- ^ As هاوائي وألاسكا were not yet U.S. states, they are included in the parenthetical figures.
- ^ first Canadian to attain the rank of full general
- ^ Australia casualties
Included in total are 55,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[1]-.
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.[2]-
Totals include 2,005 military deaths during 1919-21[3]-. The 1922 War Office report listed 59,330 Army war dead[4]. - ^ Belgium casualties
Included in total are 35,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[5] Figures include 13,716 killed and 24,456 missing up until Nov.11, 1918. "These figures are approximate only, the records being incomplete." [6]. - ^ Canada casualties
Included in total are 53,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds.[7]
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.[8]
Totals include 3,789 military deaths during 1919-21 and 150 Merchant Navy deaths[9]-. The losses of Newfoundland are listed separately on this table. The 1922 War Office report listed 56,639 Army war dead[10]. - ^ France casualties
Included in total are 1,186,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[11]. Totals include the deaths of 71,100 French colonial troops. [12]-Figures include war related military deaths of 28,600 from 11/11/1918 to 6/1/1919.[13] - ^ Greece casualties
Jean Bujac in a campaign history of the Greek Army in World War One listed 8,365 combat related deaths and 3,255 missing[14], The Soviet researcher Boris Urlanis estimated total dead of 26,000 including 15,000 military deaths due disease[15] - ^ India casualties
British India included present-day India, Pakistan and Bangladesh.
Included in total are 27,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[16].
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.[17]
Totals include 15,069 military deaths during 1919-21 and 1,841 Canadian Merchant Navy dead[18]. The 1922 War Office report listed 64,454 Army war dead[19] - ^ Italy casualties
Included in total are 433,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[20]
Figures of total military dead are from a 1925 Italian report using official data[21]. - ^ War dead figure is from a 1991 history of the Japanese Army[22].
- ^ New Zealand casualties
Included in total are 14,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[23].
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.[24]
Totals include 702 military deaths during 1919-21[25]. The 1922 War Office report listed 16,711 Army war dead[26]. - ^ Portugal casualties
Figures include the following killed and died of other causes up until Jan.1, 1920; 1,689 in France and 5,332 in Africa. Figures do not include an additional 12,318 listed as missing and POW[27]. - ^ Romania casualties
Military dead is "The figure reported by the Rumanian Government in reply to a questionnaire from the International Labour Office"[28]. Included in total are 177,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[29]. - ^ Russia casualties
Included in total are 1,451,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[30]. The estimate of total Russian military losses was made by the Soviet researcher Boris Urlanis.[31] - ^ Serbia casualties
Included in total are 165,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[32].The estimate of total combined Serbian and Montenegrin military losses of 278,000 was made by the Soviet researcher Boris Urlanis[33]
- ^ South Africa casualties
Included in total are 5,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[34]
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.[35]
Totals include 380 military deaths during 1919-21[36]. The 1922 War Office report listed 7,121 Army war dead[37]. - ^ UK and Crown Colonies casualties
Included in total are 624,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds[38].
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.[39]
Military dead total includes 34,663 deaths during 1919-21 and 13,632 British Merchant Navy deaths[40]. The 1922 War Office report listed 702,410 war dead for the UK[41], 507 from "Other colonies"[42] and the Royal Navy (32,287)[43].
The British Merchant Navy losses of 14,661 were listed separately [44]; The 1922 War Office report detailed the deaths of 310 military personnel due to air and sea bombardment of the UK[45]. - ^ United States casualties
Official military war deaths listed by the US Dept. of Defense for the period ending Dec. 31, 1918 are 116,516; which includes 53,402 battle deaths and 63,114 other deaths.[46], The US Coast Guard lost an additional 192 dead [47]. - ^ "Peace Conference Delegates at Paris". American Journal of International Law. 13 (1): 79–81. January 1919. JSTOR 2187975. OCLC 482602928. Newfoundland Prime Minister Sir William F. Lloyd was a British Empire delegate at Versailles.
- ^ "World War I Ends in Andorra". The New York Times. UPI. 25 September 1958. p. 66.
المراجع
- ^1 The War Office (2006) [1922]. Statistics of the military effort of the British Empire during the Great War 1914—1920. Uckfield, East Sussex: Military and Naval Press. ISBN 1-84734-681-2. OCLC 137236769.
- ^2 Gilbert Martin (1994). Atlas of World War I. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-521077-8. OCLC 233987354.
- ^3 Tucker Spencer C (1999). The European Powers in the First World War: An Encyclopedia. New York: Garland. ISBN 0-8153-3351-X.
- ^4 The Commonwealth War Graves Commission. "Annual Report 2005-2006" (PDF).
- ^5 The Commonwealth War Graves Commission. "Debt of Honour Register".
- ^6 Urlanis Boris (2003) [1971]. Wars and Population. Honolulu: University Press of the Pacific. OCLC 123124938.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|original-place=ignored (help) - ^7 Huber Michel (1931). La population de la France pendant la guerre, avec un appendice sur Les revenus avant et après la guerre (in French). Paris. OCLC 4226464.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^8 Bujac Jean Léopold Emile (1930). Les campagnes de l'armèe Hellènique 1918-1922 (in French). Paris: Charles-Lavauzelle. OCLC 10808602.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^9 Mortara Giorgio (1925). La Salute pubblica in Italia durante e dopo la Guerra (in Italian). New Haven, Connecticut: Yale University Press. OCLC 2099099.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^10 Harries Merion, Harries Susie (1991). Soldiers of the Sun - The Rise and Fall of the Imperial Japanese Army. Random House. ISBN 0-679-75303-6. OCLC 32615324.
- ^11 Clodfelter Michael (2002). Warfare and Armed Conflicts : A Statistical Reference to Casualty and Other Figures, 1500-2000 (2nd ed.). London: McFarland. ISBN 0-7864-1204-6. OCLC 48066096.
المصادر
- Ellis, John and Mike Cox. The World War I Databook: The Essential Facts and Figures for All the Combatants (2002)
- Esposito, Vincent J. The West Point Atlas of American Wars: 1900-1918 (1997) despite the title covers entire war; online maps from this atlas
- Falls, Cyril. The Great War (1960), general military history
- Higham, Robin and Dennis E. Showalter, eds. Researching World War I: A Handbook (2003), historiography, stressing military themes
- Pope, Stephen and Wheal, Elizabeth-Anne, eds. The Macmillan Dictionary of the First World War (1995)
- Strachan, Hew. The First World War: Volume I: To Arms (2004)
- Trask, David F. The United States in the Supreme War Council: American War Aims and Inter-Allied Strategy, 1917-1918 (1961)
- Tucker, Spencer, ed. The Encyclopedia of World War I: A Political, Social, and Military History (5 volumes) (2005), online at eBook.com
- Tucker, Spencer, ed. European Powers in the First World War: An Encyclopedia (1999)